
Exhibit 99.2

© 2020 BiomX LTD. All rights reserved Company Introduction

Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains certain “forward - looking statements” within the meaning of the “safe harbor” provisions of the U . S . Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 . Forward - looking statements can be identified by words such as : “target,” “believe,” “expect,” “will,” “may,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “would,” “positioned,” “future,” and other similar expressions that predict or indicate future events or trends or that are not statements of historical matters . Forward - looking statements are neither historical facts nor assurances of future performance . Instead, they are based only on BiomX management’s current beliefs, expectations and assumptions . When we discuss our ability to quickly generate clinical proof of concept in patients and the advantages of our BOLT platform, our leadership position in phage technology and timing of, among other things, clinical trials initiations, conclusion and receipt of results and meeting milestones relating to our development plan as well as commercialization plans, we are making forward - looking statements . Because forward - looking statements relate to the future, they are subject to inherent uncertainties, risks and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict and many of which are outside of our control . Actual results and outcomes may differ materially from those indicated in the forward - looking statements . Therefore, you should not rely on any of these forward - looking statements . You should review additional disclosures we make in our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), which are available on the SEC’s website at www . sec . gov . Except as required by law, we are under no duty to (and expressly disclaim any such obligation to) update or revise any of the forward - looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise . 2

We develop disease modifying therapies based on natural or engineered phage cocktails as precision medicines to target and specifically destroy harmful bacteria What we do 3 Our R&D platform enables generation of clinical proof of concept in patients within 12 - 18 months from project initiation * * In certain indications the length of clinical validation may be longer depending on indication, identity of target bacteria , r ecruitment rate, cohort size and other factors.

Unique position as leader in phage technology 4 Technology • BOLT phage therapy platform – Rapid path from discovery to clinic • Scalable in - house manufacturing – can support annually over 50 different phage at a clinical grade • Acne collaboration with leading global cosmetic company • Biomarker discovery collaborations in IBD • Janssen (J&J) • Boehringer Ingelheim Partnerships Pipeline Financing and investors • Approximately $ 60 M raised in 2 private rounds • October 2019 public listing ( NYSE:PHGE ) and raising an additional $ 60 M 1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) , Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC). 2. Phase 2 results in acne, Phase 1b/2a results in cystic fibrosis, Phase 2 results in atopic dermatitis, Phase 1b/2a results in IBD/PSC Only clinical stage phage company focusing on chronic indications • P ositive P hase 1 data for topical delivery of BX 001 in subjects with acne prone skin • Positive Phase 1 a data of pharmacokinetic study for IBD/PSC 1 evaluating oral delivery • 4 Phase 2 readouts expected by mid 2022 2

Phage: Nature’s precision tool to target bacteria Each phage binds only to specific bacterial strains Phage have an amplifying lifecycle Locate Inject Infect Multiply Assemble Eradicate Seek 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 Source: Kortright et al. (2019), Cell Host & Microbe

Oncology • Colorectal Cancer – F. nucleatum • Gastric Cancer – H. pylori Other • Acne – C. acnes • Liver Disease - E. faecalis Multiple potential applications of phage therapy 6 Immune mediated • Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) – K. pneumoniae • Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) - K. pneumoniae • Atopic Dermatitis – S. aureus Infectious diseases • Cystic Fibrosis - P. aeruginosa • Carbapenem Resistance - K. pneumoniae

Phage discovery Preclinical Phase I Phase II Phase III Product Candidates Acne • BX001 1 (Cosmetic route) IBD/PSC • BX003 2 Cystic fibrosis • BX004 Atopic dermatitis • BX005 Colorectal cancer Pipeline • Positive Phase 1 a results ( 1 Q 2021 ) • Phase 1 b/ 2 a results expected 2 Q 2022 • Positive Phase 1 results (1Q 2020) • Phase 2 results exp. 3Q and 4Q 2021 7 • Animal model results expected 2 Q - 3 Q 2021 • Phase 1b/2a part 1 results expected 1Q 2022, part 2 expected 2Q 2022 (1) BX001 is intended to be developed and commercialized as a cosmetic (2) In November 2020, BiomX announced the consolidation of its IBD and PSC programs to develop one broad host range product candidate for both IBD and PSC, designated BX003 (replacing a previous phage product candidate for IBD named BX002) • Phase 2 results expected in 1 H 2022

Our platform allows clinical POC within 12 - 18 months 8 Target Bacteria Target Validation Phage Synthetic Engineering (optional) Cocktail Optimization Discovery & Characterization Manufacturing & Formulation Phage Therapy 3 Clinical testing 1). Strong safety profile of naturally occurring phage supported by regulatory feedback allows proceeding to Phase 2 studies without preclinical safety studies or Phase 1 studies in healthy volunteers. 2). In certain indications the length of clinical validation may be longer depending on indication, identity of target bacter ia, recruitment rate, cohort size and other factors. 3) Usually, we would develop an optimized phage therapy, which is comprised of several phage (a phage cocktail) optimized to address multiple characteristics such as bacteri al host range, emergence of resistance and other factors. In some cases, we may alternatively develop personalized phage cocktails tailored to target specific strain/s of a given patient. We may complete a clinical POC by treating multiple patients with either an optimized phage cocktail or personalized cocktails C linical POC in patients enabled within 12 - 18 months 1,2 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Traditional pharma drug development Phage therapy Discovery CMC Tox Phase 1 Phase 1/2 Phase 2 Phage cocktail

Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Upcoming milestone: Phase 1b/2a data expected in 2Q 2022

10 Pro - inflammatory Klebsiella strains affect IBD pathology Inflammatory induction is seen in GF mice* Higher abundance of Klebsiella strains in IBD patients IFN - g IFN - g G F + 7 o ther m ix G F + t arget s train TH 1 % r elative Abundance Abundance of Klebsiella strains Activity of bacterial target confirmed by BiomX IBD • Identifying potential disease causing pro - inflammatory Klebsiella strains Disease s tate Induce i nflammation Source: Atarashi et al. ( 2017 ), Science * TH 1 – A lineage of CD 4 + effector T cell secreting IFNg and TNF. In IBD, TH 1 cells accumulate in the intestinal tract of IBD patients and are directly associated with disease Klebsiella strains CD – Crohn’s disease UC – Ulcerative colitis GF – Germ Free

11 Source: Nakamoto et al. (2019), Nature Microbiology *TH17 – A lineage of CD4+ effector T cell secreting IL17A +, promoting inflammation and fibrosis within the liver PSC • Klebsiella identified as possible driver of “leaky gut” Discovery approach Klebsiella pneumoniae (KP) is a specific gut pathobiont of PSC that is an intestinal barrier disrupter and is pro - inflammatory ( “ leaky gut ” ) KP isolated from mice ’ s lymph nodes colonized with patient samples Th17* is induced in livers of GF mice inoculated with fecal samples from PSC patients GF mice Humanized microbiota mice Analysis of immune response Fecal samples from PSC patients Healthy PSC patients Colitis patients Klebsiella pneumoniae plays a gating role SPF – Specific - pathogen - free HC – Healthy Controls PSC/UC – PSC and ulcerative colitis

Phage cocktail composition drives activity 12 Source: Internal data 1 st - generation phage cocktail (in - vivo) 2 nd - generation phage cocktail (in - vivo) reduces bacterial load Control 2 nd - gen cocktail Application of phage Fecal bacterial load Mucosa * *P< 0.05 ; **P < 0.001 ** Phage cocktail Control 0 2 4 6 8 10 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 Day from inoculation C F U / g r s t o o l *P < 0.01 LOD 1 st - gen cocktail Control Application of phage Fecal bacterial load * Adding 2 phage with new MOA Phage cocktails are optimized to prevent appearance of resistant bacteria by targeting multiple bacterial receptors and defense mechanisms

13 BX 002 : Phase 1 a pharmacokinetic results demonstrate delivery of high levels of viable phage to the gut 1 (1) Study conducted with BX 002 , a phage therapy candidate for oral administration targeting K. pneumoniae . In November 2020 , BiomX announced the consolidation of its IBD and PSC programs to develop one broad host range product candidate for both indication s, designated BX 003 . ( 2 ) PFU – Plaque forming units. ( 3 ) Value is based on median levels of K. Pneumoniae measured in clinical stool samples collected by BiomX from IBD patients. Time (days) Results - Median levels of viable phage detected in stool prior and following oral delivery of phage Baseline Treatment Follow up Median PFU 2 levels measured in stool (per day) ~ 10 3 Median levels 3 of target bacteria in IBD patients (~ 10 7 ) Phase 1 a study design 3 - day multiple - dose study (placebo - controlled) • Objectives • Safety and pharmacokinetics • Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Detection of viable phage in stool • Study Population: Healthy volunteers • 18 subjects • Oral delivery • 14 phage treatment + 4 placebo • BX 002 was safe and well tolerated • Viable phage delivered is ~ 1,000 times higher compared to bacterial burden of K. pneumoniae in IBD patients

Stool t est Phage treatment Identify presence of K. pneumoniae using companion diagnostic 14 In November 2020 , BiomX announced the consolidation of its IBD and PSC programs to develop one broad host range product candidate for both in dic ations, designated BX 003 . Phase 1 b/ 2 a study design Proof - of - Principle 4 - week dosing study (placebo - controlled) • Objectives • Safety and efficacy • Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Reduction of K. pneumoniae (efficacy) • Stool microbiome evaluation • Study Population: Target bacteria carriers (Healthy volunteers or IBD/PSC patients ) • 60 subjects total • Oral delivery • BX 003 or placebo • 30 subjects per cohort Data expected 2 Q 2022 Patient A Target bacteria Phase 1b/2a study results expected in 2Q 2022

Cystic Fibrosis Upcoming milestone: Phase 1 b/ 2 a part 1 data expected in 1 Q 2022

Recurring infections leading to antibiotic resistance are a main cause of death in CF 16 1. CF Foundation, Bomberg et al., 2008 2. Vertex 10 K filing 2020 , internal estimates Phases of P. aeruginosa infection in CF 1 Antibiotics Antibiotics Antibiotics Antibiotics Antibiotics Initial Intermittent Chronic Clonal selection Biofilm formation Genotype/phenotypic adaptation Infancy Childhood Adolescence / Adulthood Limit of detection P . a eruginosa density in sputum Repeated antibiotic courses lead to nonmucoid and mucoid multidrug - resistance (MDR) of P. aeruginosa strains • CF patients regularly use multiple therapies – CFTR modulators, anti - infectives, mucolytic agents, bronchodilators and other • Worldwide CF therapeutic market in 2020 was approximately $ 8.5 B

Selected cases of compassionate use of phage therapy targeting P. aeruginosa 17 2 CF patients, Georgia 1,2 • 5 yr old & 7 yr old • N ebulized phage • Combined with antibiotics • 9 courses with 4 - 6 week intervals • Reduction in sputum bacterial burden noted ( 10 7 10 4 CFU/g) 2 • Patient gained weight, clinical improvement observed 1 CF patient, San Diego, US 3 11 CF patients treated with phage targeting P. aeruginosa 1 Kutateladze et al., 2008 2 Kvachadze et al., 2011 3 Law et al., 2019 4 Stanley et al., 2020 8 CF patients, Yale University, US 4 • 26 yr old • Phage administered IV • Combined with antibiotics • No exacerbation within 100 days following the end of phage therapy • eIND path for 8 CF patients • N ebulized phage • 7 - 10 days, single or multiple rounds • Post phage therapy P. aeruginosa CFU titers decreased significantly ( 2.2 ± 0.76 log reduction) • Post phage therapy FEV 1 % changed in a range between 0 to 8.9 % Results demonstrate the potential of phage therapy to decrease bacterial burden and improve FEV 1

** ** Bacterial count Colony forming units / well 18 BX 004 is active on antibiotic resistant P. aeruginosa strains and penetrates biofilm in vitro C o n t r o l I m i p e n e m 2 0 0 g / m L P h a g e c o c k t a i l 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 BX 004 displays enhanced biofilm penetration compared to antibiotics ** BX 004 penetrates biofilm in vitro 1 BX 004 Control Biofilm was grown from P. aeruginosa for 24 hours and then treated with BX 004 for 6 hours (control - untreated wells). Treatment with antibiotics not shown Cr ystal v iolet – Used for biomass staining of biofilm. Staining substantially reduced following treatment with BX 004 **p - value < 0.001 1. Internal data. A P. aeruginosa strain sensitive to antibiotics was grown to form biofilm 2. Imipenem 200 micrograms/ml (X 100 MIC), (β - lactam antibiotic with activity against P. aeruginosa)

19 P hase 1 b/ 2 a study targeting P. aeruginosa with first readout in 1 Q 2022 Phase 1 b/ 2 a – Part 1 Objectives • Safety, PK and microbiologic/clinical activity • Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Decrease in P. aeruginosa burden • Sputum pharmacokinetics • FEV 1 (forced expiratory volume) • CFQ - R (CF Questionnaire - Revised) and CRISS Study Population • CF patients with chronic P. aeruginosa infection 8 Subjects • 6 receive nebulized BX 004 • 2 receive nebulized placebo • 6 days duration of treatment Key Design Features • Single ascending dose followed by multiple doses Data expected 1 Q 2022 Phase 1 b/ 2 a – Part 2 Data expected 2 Q 2022 Objectives • Safety and efficacy Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Decrease in P. aeruginosa burden • FEV 1 (forced expiratory volume) • CFQ - R (CF Questionnaire - Revised) and CRISS Study Population • CF patients with chronic P. aeruginosa infection 21 subjects • Nebulized BX 004 phage therapy or placebo • 2:1 randomization • 10 days duration of treatment

Upcoming milestone: Phase 2 data expected in 1 H 2022 Atopic Dermatitis

Atopic Dermatitis (AD) flares are associated with presence of S. aureus Relative abundance of staphylococcal species on skin during AD disease stages (metagenomics analysis) Control = healthy skin Baseline = routine AD disease state Flare = worsening in the clinical severity of the typical AD, without usage of skin - directed antimicrobial and anti - inflammatory treatments for seven days Post flare = 10 – 14 days after initiation of skin - directed therapies Individuals Mean relative abundance Control Baseline Flare Post - flare Byrd and Kong ( 2017 ) Sci Transl Med. 05 9 ( 397 ) S. aureus becomes the dominant bacterial species during AD flares and is correlated with SCORAD

22 Proinflammatory mechanisms Such as, protein A and superantigens (enterotoxins) which trigger inflammatory responses and cytokine release Kong, H.H. et al , ( 2012 ), Genome research . Byrd, A.L. et al , ( 2017 ) Science translational medicine S. aureus contributed to pathogenicity through multiple virulence factors Alpha - toxin forms pores in keratinocytes and proteases facilitate dissolution of the stratum corneum. Barrier disfunction S. aureus has developed several surface molecules to adhere to the human stratum corneum Adhesion
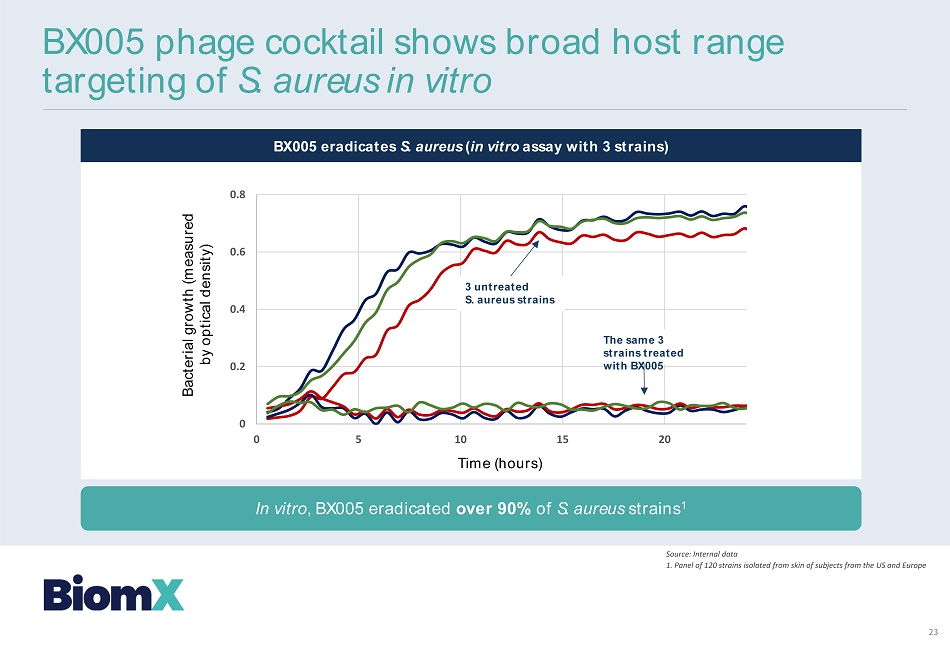
BX 005 eradicates S. aureus ( in vitro assay with 3 strains) Time (hours) Bacterial growth (measured by optical density) BX 005 phage cocktail shows broad host range targeting of S. aureus in vitro Source: Internal data 1 . Panel of 120 strains isolated from skin of subjects from the US and Europe In vitro , BX 005 eradicated over 90 % of S. aureus strains 1 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 0 5 10 15 20 3 untreated S. aureus strains The same 3 strains treated with BX 005 23

24 Data expected 1 H 2022 Phase 2 study results targeting S. aureus expected in 1 H 2022 Study design • Objectives • Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics • Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Decrease in target bacteria • Clinical improvement (e.g. change in EASI/IGA scores) • Study Population • Atopic dermatitis patients • S. aureus colonized • 8 0 subjects • BX 005 or placebo (vehicle) administered topically • 8 - week duration of treatment BX 005 /Placebo Applications: Sampling: First application Last application Topical administration Baseline 8 weeks 4 weeks 9 weeks 8 weeks 1 week

Acne Upcoming milestone: Phase 2 data expected in 3 Q and 4 Q 2021 (cosmetic study)

BX 001 : Phage cocktail attributes BX 001 A topical gel containing natural phage against C. acnes to modulate skin microbiome 26 * Source: Internal data, in vitro results Phage cocktails penetrate biofilm ( in vitro ) • Active against antibiotic - resistant strains* • Penetrates biofilm*

27 BX 001 /Placebo Applications: Sampling: 2 weeks 2 weeks First application Last application Once daily Baseline 4 weeks 2 weeks 5 weeks 1 week BX 001 : Phase 1 clinical trial design Phase 1 – Completed 4 - week study (placebo - controlled) • Primary endpoint • Safety & Tolerability • Exploratory endpoints • Reduction of C. acnes (efficacy) • Skin microbiome evaluation • 75 subjects • 2 doses (high and low dose) + placebo (vehicle) • 25 subjects per cohort

28 BX 001 : Phase 1 results demonstrate statistically significant reduction in C. acnes levels • Both high and low doses demonstrated excellent safety and tolerability • Findings on the high sebum subgroup support enrichment of study population in the Phase 2 study ( 1 ) Measured by qPCR. Cutibacterium acnes (or C. acnes) comprised over 98 % of Cutibacterium spp. ( 2 ) Subjects were divided into high and low sebum level groups based on median level of sebum at baseline ( 133 µg/cm 2 ) 0.22 log* difference - high dose Vs. control * p= 0.036 Cutibacterium levels qPCR Log 10 (copies/sample) * V i s i t 2 ( B a s e l i n e ) V i s i t 3 ( d a y 1 4 ) V i s i t 4 ( d a y 2 8 ) V i s i t 5 ( d a y 3 5 ) -0.4 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 BMX-01-003 M e a n c h a n g e f r o m b a s e l i n e i n C u t i b a c t e r i u m q P C R L o g 1 0 ( C o p i e s / s a m p l e ) BX001 10 7 BX001 10 9 Vehicle 0.4 log* difference - high dose Vs. control * p< 0.008 Cutibacterium levels qPCR Log 10 (copies/sample) Change in level of Cutibacterium 1 – All subjects Change in level of Cutibacterium 1 – High sebum subgroup 2

BX 001 /Placebo Applications: Sampling: 12 weeks First application Last application Baseline 12 weeks 8 weeks 13 weeks 1 week 29 BX 001 phase 2 cosmetic study results expected in 2 H 2021 Phase 2 Study Design 12 - week application, Placebo - controlled • Objectives • Safety and efficacy • Endpoints • Safety and tolerability • Reduction of C. acnes (efficacy) • Skin microbiome evaluation • IGA and lesion numbers (efficacy) • 140 subjects • Phage or placebo (vehicle) • 70 subjects per cohort • 8 - week data expected 3 Q 2021 • 12 - week data expected 4 Q 2021

Colorectal Cancer Upcoming milestone: Proof of concept in animal models by 2 Q - 3 Q 2021

31 + = Immune checkpoint inhibitors Effect on tumor “ Cold ” tumor “ Hot ” tumor + = Immune checkpoint inhibitors Effect on tumor Sources: Vareki ( 2018 ), Journal for immunotherapy of Cancer; Galon et al. ( 2019 ), Nature Reviews/Drug Discovery Most c olorectal c ancer (CRC) patients do n ot respond to immunotherapy

32 Bacteria residing inside t umors offer a novel targeted intervention to “ uncloak ” t umors to “ hot ” Numerous observations of bacteria residing inside tumors F. nucleatum Tumor x 30 x 10 ISH, red= F. nucleatum Representative RNA - In - situ hybridization images showing patterns of F. nucleatum localization in human rectal cancer tissue samples F. nucleatum is found in over 80 % of colorectal cancer tumors (BiomX internal analysis and public data) BiomX internal data Li YY, Ge QX, Cao J, et al. ( 2016 ) World J Gastroenterol. Bachrach et al. ( 2016 ), Cell Host & Microbe Serna et al. ( 2020 ) Annals of Oncology Kostic et al. ( 2013 ), Cell Host & Microbe

33 Engineered p hage are designed to deliver p ayloads to bacteria in tumors Phage are designed to carry payloads to intra - tumor bacteria Phage cocktail with a payload turns cold tumors into hot Add payload using SynBio + new gene Phage cocktail Phage cocktail + = Immune checkpoint inhibitors Effect on tumor “ Cold ” tumor “ Cold ” tumor “ Hot ” tumor + = Immune checkpoint inhibitors Effect on tumor Phage cocktail IV Payloads : IL - 15 , GM - CSF, Cytosine Deaminase

Key development milestones 34 FN14 FN14+Phages Phages only 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 P h a g e s i n 1 g t u m o r CT - 26 2 x 10 5 /mouse (SC) 1 FN 14 (IV) 12 Phage treatment (IV) 15 Day: 18 IL - 15 - engineered phage w.t. phage NTC , 1,000 750 250 Base pairs: IL 15 insertion into phage w.t. phage IL-15 - phage 0 1000 2000 3000 Luminescence (IL-15-Hibit) R L U Luminescence (AU) IL - 15 expression in bacteria WT phage Engineered phage CT - 26 2 x 10 5 /mouse (SC) 1 18 FN 14 (IV) 12 Phage treatment (IV) 23 15 7 10 Day: Anti PD - 1 treatment (IP) 13 Survival, Tumor growth rate 16 19 IV delivery of phage to intra - tumor bacteria ( in - vivo ) IL - 15 payload engineered into F. nucleatum phage ( in - vitro ) Impact of engineered phage + anti - PD 1 in CRC mouse model Engineered Payloads: IL - 15 , GM - CSF, Cytosine Deaminase Planned 2 Q - 3 Q 2021 Phage per 1 gram tumor Source: Internal data

35 2 H 20 1 H 20 2 H 21 1 H 21 Cash, cash equivalents and short - term deposits as of March 31 st , 2021 were $ 53.6 M million 2 H 22 1 H 22 1. Phase 2 results in acne, Phase 1 b/ 2 a results in cystic fibrosis, Phase 2 results in atopic dermatitis, Phase 1 b/ 2 a results in IBD/PSC 2. Our acne product is developed under a cosmetic regulatory path and we currently do not anticipate any additional clinical tri als beyond the Phase 2 study. 3. As the IBD and PSC programs share the same bacterial target, Klebsiella pneumoniae, we currently anticipate that the BX 003 phage cocktail will be developed for both indications. Accordingly, the Phase 1 study is expected to support progress of both indications. Key Catalysts: 4 Phase 2 readouts by mid 2022 1 Acne 2 IBD/PSC 3 Atopic Dermatitis CF Mfg. Phase 2 results Phase 2 initiation Pre - commercial Pre - commercial Phase 1 Results Phase 1 a initiation Mfg. Phase 1 a results Mfg . Phase 1 b/ 2 a results CMC Phage discovery Phase 1 b/ 2 a initiation Cocktail optimization Mfg Phase 1 b/ 2 a results –––– Phage discovery Mfg Cocktail optimization Mfg. Phase 2 results –––– CRC Initiate in vivo studies In vivo results In vivo results Mfg Cocktail optimization Phage engineering

Assaf Oron CBO Former CBO of Evogene, an agricultural biotechnology company; raised $ 85 M in NYSE listing. Executed transactions with turnover of >$ 100 M with global seed companies Marina Wolfson, CPA SVP Finance & Operations Most recently principle financial officer of Bioview (TASE:BIOV). Former senior auditor at E&Y working with large pharmaceutical and hi - tech companies, VCs and start - ups Inbal Benjamini - Elran VP Human Resource 15 years experience in executive HR roles globally. Former head of HR at Herzog law firm and HR director at Teva Europe (NYSE:TEVA) Experienced leadership team 36 Management Team Scientific Founders Prof. Timothy K. Lu Prof. Eran Elinav Prof. Rotem Sorek Jonathan Solomon CEO and Board Member Former co - founder, president, and CEO of ProClara for treating neurodegenerative diseases; raised > $ 100 M. Harvard Business School grad. Service in an elite IDF unit Sailaja Puttagunta , MD CMO Infectious disease physician (Yale graduate), Developed several antibiotics through all clinical development stages under Allergan, Pfizer, Durata and other biotechs Merav Bassan , PhD CDO Over 20 years of early and clinical drug development experience at Teva Pharmaceuticals and small biotechs . Most recently served as VP of translational sciences at Teva

Experienced leadership team 37 Board of Directors Director, Jonas Grossman Director, Gbola Amusa, MD Chairman, Russell Greig, PhD Director, Alan Moses, MD Director, Jonathan Solomon Director, Lynne Sullivan Director, Paul Sekhri

THANK YOU